2 Minuti di Scienza: Come si misura clinicamente la gravità dei sintomi in pazienti atassici
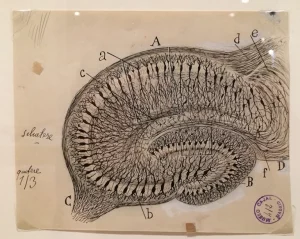
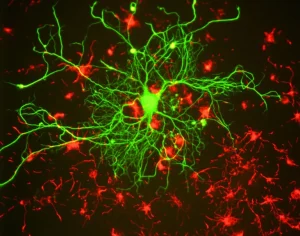
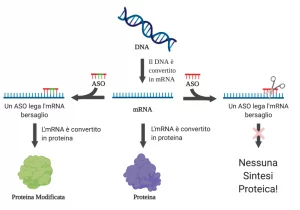
Il coordinare facilmente ed efficacemente movimenti come il parlare e il camminare è essenziale nello svolgimento della vita quotidiana. L’abilità di orchestrare questi movimenti con successo è generalmente chiamata “coordinazione mootoria”. Anche se i pazienti di SCA in genere sono in grado di iniziare movimenti coorporei, la loro abilitá di Read More…